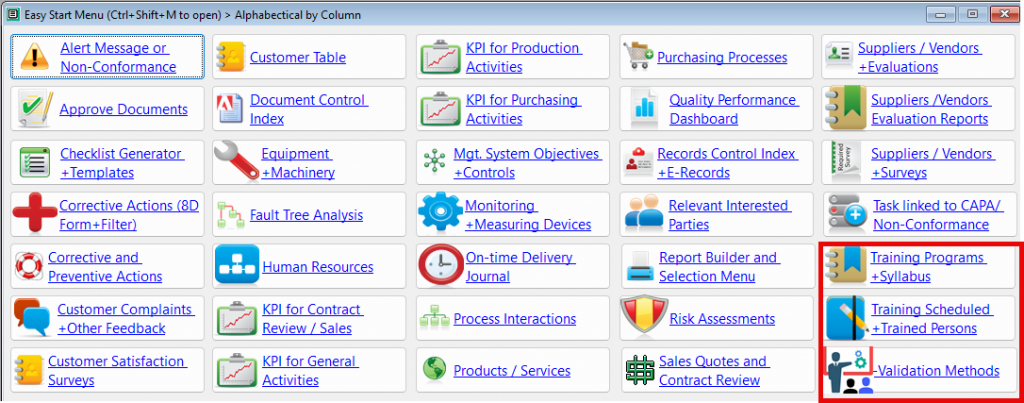
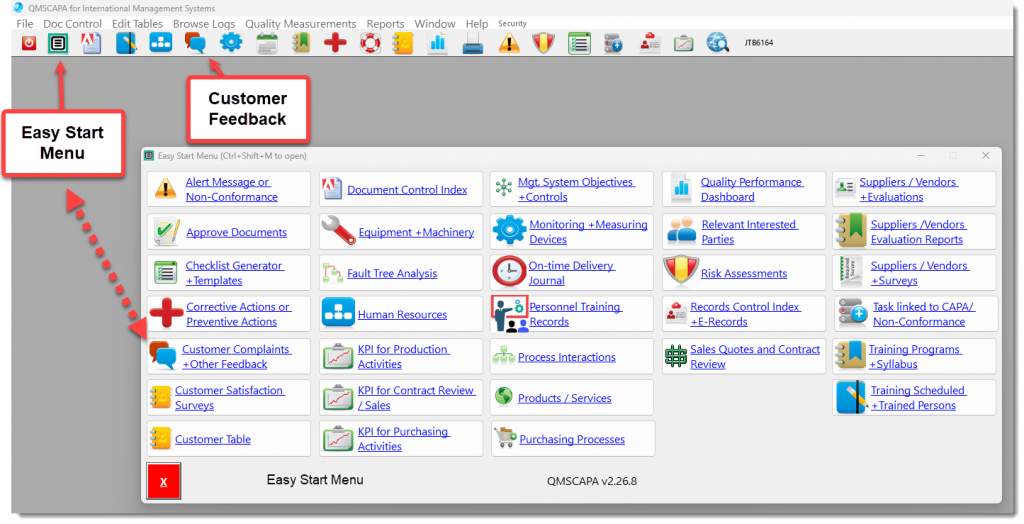
How QMSCAPA is Helping Small to Large Businesses Improve their Quality Management System
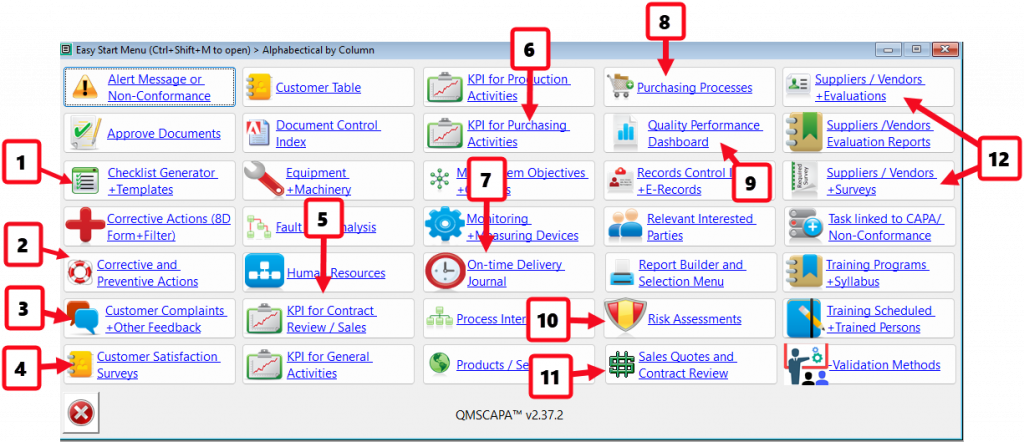
- Checklist Generator for Evaluating Business Opportunities and Process.
- Module for managing Corrective and Preventive Actions.
- Module for managing Customer Complaints and other feedback.
- Module for Evaluating Customer Satisfaction.
- Monitoring & Measuring KPI for Contract Review and Sales Processes.
- Monitoring & Measuring KPI for Purchasing Processes, including on-time delivery by suppliers.
- Monitoring & Measuring KPI for on-time delivery to customers.
- Module for managing Purchasing Processes.
- Quality Performance Dashboard for report KPI results and Continual Improvement.
- Module for managing Risk Assessments with Interested Parties
- Module for managing Sales Quotes, Contract Review and Production Work Orders.
- Module for managing and evaluating Supplier Performance, including Quality Surveys with Suppliers.
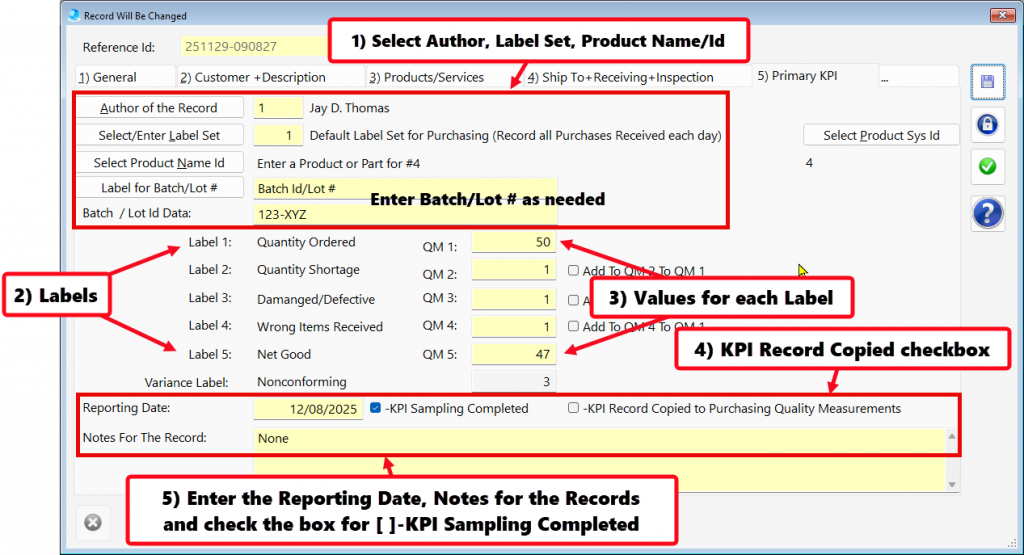
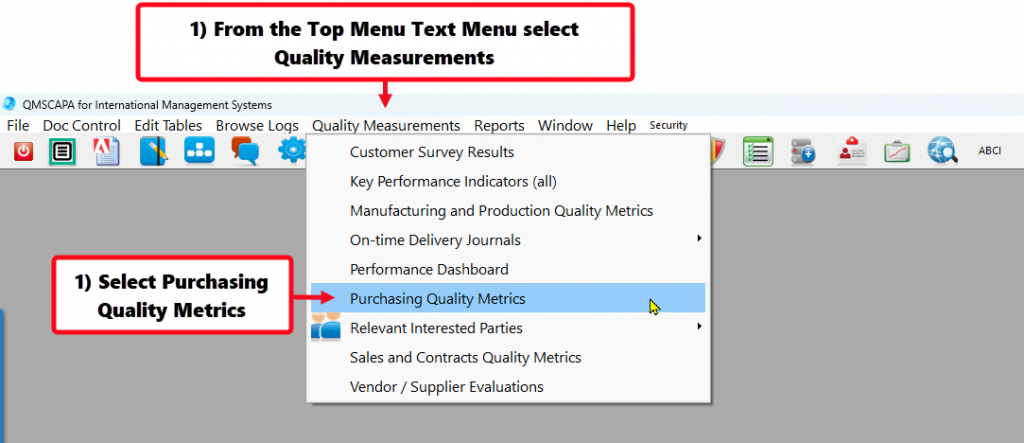
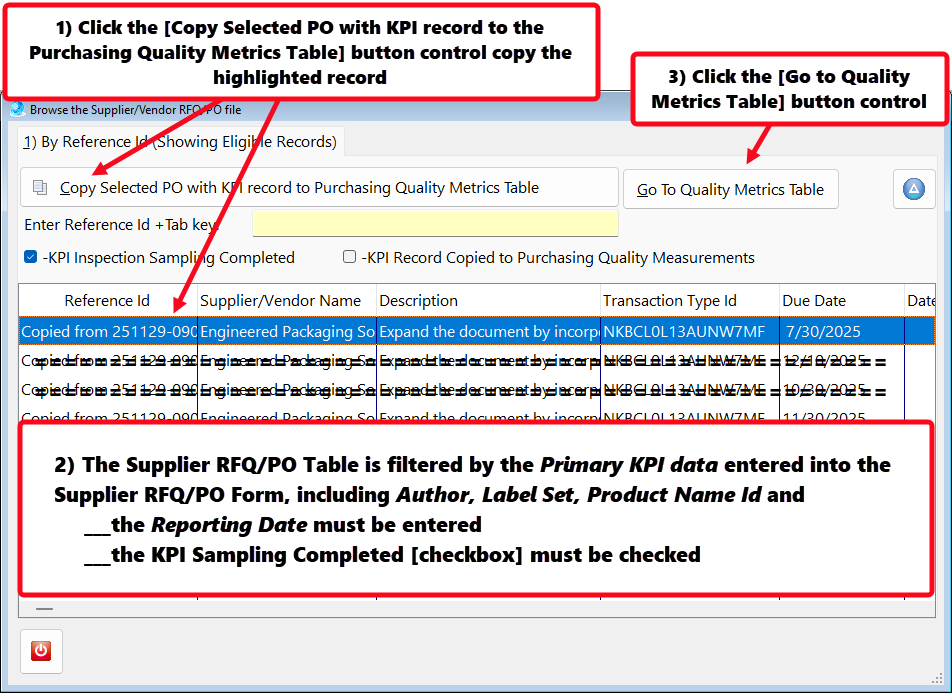
Recording Supplier On-time Delivery in the Purchasing Quality Module
In Quality Management Systems, such as AS9100 and ISO 9001, the Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis, and Evaluation of Suppliers become even more powerful when applied specifically to Purchasing and Supply Chain Management, because suppliers are often the largest source of variation, risk, and customer dissatisfaction in both AS9100 and ISO 9001. Applying the discipline of Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis, Evaluation, and Customer Satisfaction to the supply chain turns purchasing from a transactional function into a strategic quality control mechanism.
To comply with AS9100 and ISO9001—and to operate a mature Quality Management Systems—organizations must establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that quantify performance and variation.
Statistical Process Control (SPC) is one of the most powerful tools for this.
How KPIs and SPC strengthen the QMS:
- Make variation visible. Concise SPC reports and charts show whether a process is stable, trending, or out of control—something raw data cannot reveal.
- Identify root causes faster. When a KPI shows a spike or drift, SPC helps pinpoint whether the cause is common‑cause variation (systemic) or special‑cause (specific event).
- Support predictive quality. Standard deviations, control limits, and capability indices (Cp, Cpk) show whether a process can meet requirements consistently.
- Provide early warning signals. Management can intervene before defects reach the customer.
- Enable fact‑based Management Review. Leadership sees not just results, but process capability, risks, and opportunities for improvement.
Why standard deviation matters
Standard deviation quantifies how much variation exists in a process. When used in SPC:
- It defines control limits “plus or minus three sigma(±3σ), which determine whether a process is stable.
- It reveals whether a process is capable of meeting tolerance.
- It helps management distinguish between noise and meaningful signals.
- Without standard deviation and SPC, KPIs become lagging indicators—useful only after problems occur.
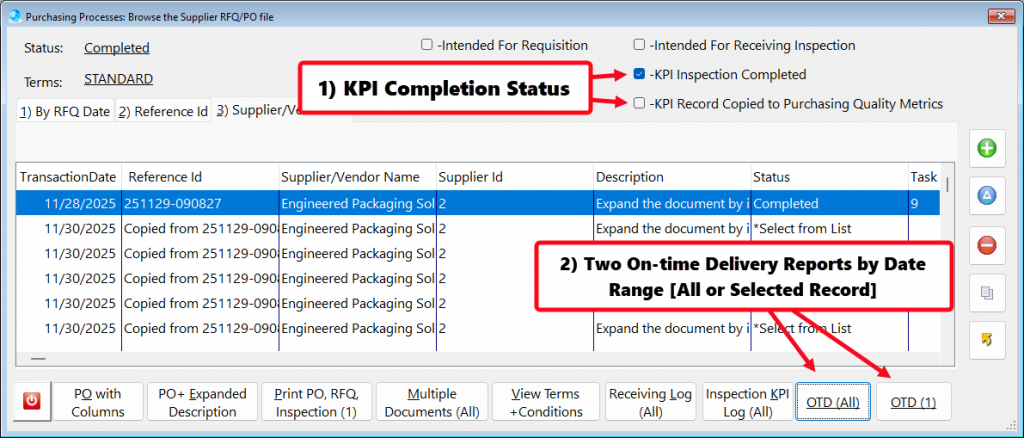
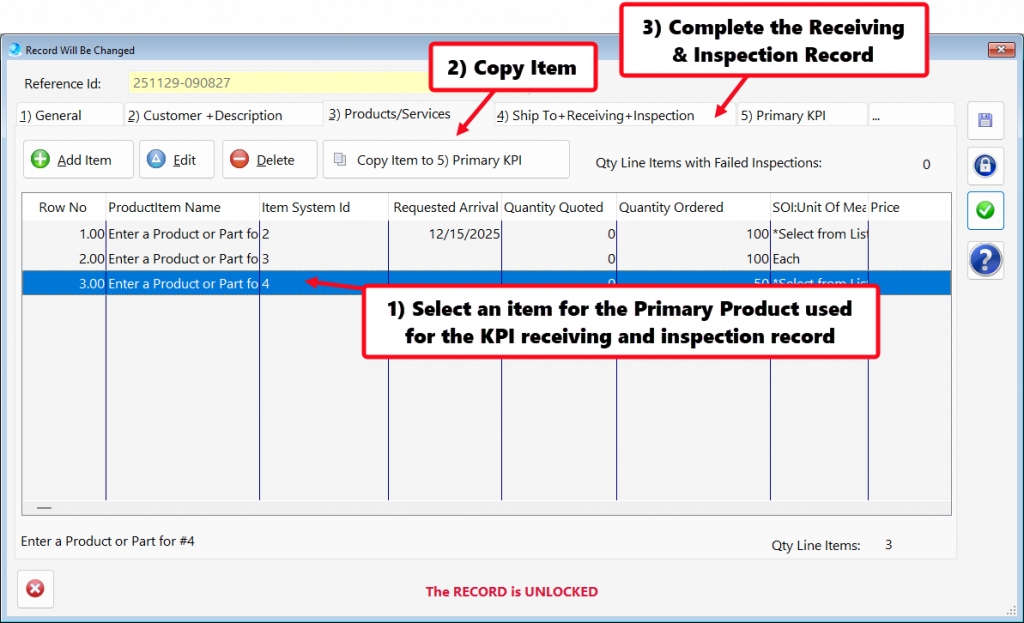
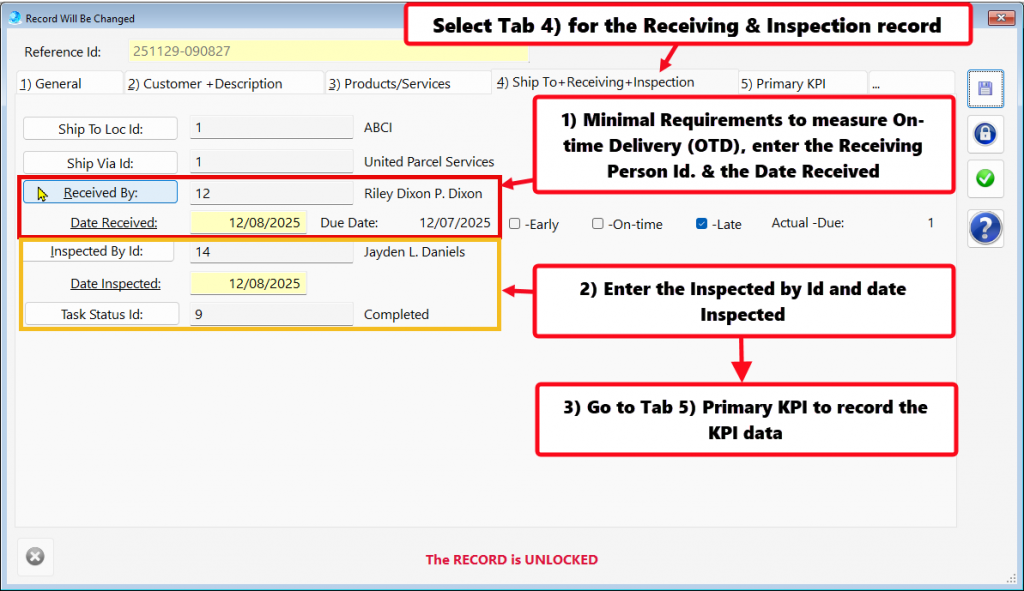
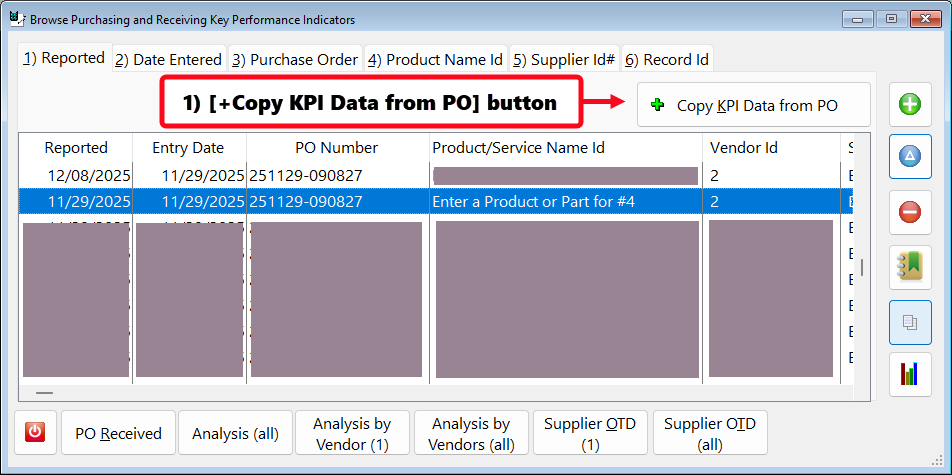
- In procurement and supply chain management, on-time delivery (OTD) from critical suppliers is a standard KPI that is closely monitored to ensure supply chain reliability.
- Tracking on-time delivery (OTD) performance for critical suppliers serves as a vital KPI in supplier management.
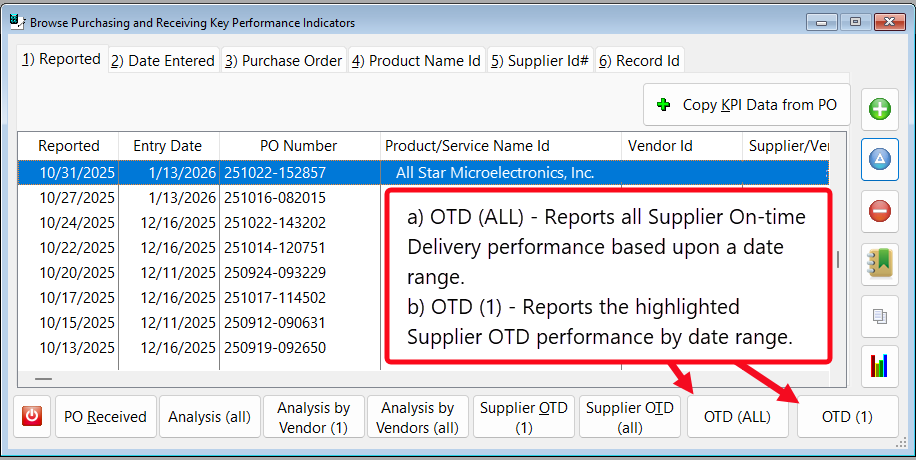
- The button [OTD (All)] – Reports all Supplier On-time Delivery performance based upon a date range.
- The button [OTD (1)] – Reports the highlighted Suppler OTD performance by date range.
Customer Sales Contract Review Processes
Customer Communication (AS9100D 8.2.1 / ISO 9001 8.2.1)
Practical methods
- Formal quoting process with controlled templates.
- Documented communication matrix defining who may speak to customers about what topics.
- Engineering change request (ECR/ECO) workflow for customer‑initiated changes.
- Customer complaint log integrated with corrective action processes.
- Project progress and production meetings for complex or high‑risk orders.
Required records which may be generated and/or maintained with QMSCAPA
- Quote records and revisions.
- Contract review, approvals required and dates
- Production Meeting minutes or kickoff notes.
- Complaint records and corrective actions.
- Engineering change documentation.
- Customer change order documentation
Determining Requirements for Products and Services (AS9100D 8.2.2 / ISO 9001 8.2.2)
What organizations must achieve
- Identify explicit, implicit, and regulatory requirements.
- Ensure requirements are complete, unambiguous, and feasible before acceptance.
Practical methods
- Technical data package (TDP) review including drawings, specifications, models, and standards.
- Regulatory applicability review (e.g., ITAR, DFARS, RoHS, REACH, special processes).
- Risk assessment for unusual materials, tolerances, or delivery expectations.
- Supplier capability review if outsourced processes are involved.
Required records which may be generated and/or maintained with QMSCAPA
- TDP review forms.
- Risk assessments (FMEA, risk log, or AS9100D‑aligned risk matrix).
- Supplier capability or special process approvals.
- Regulatory compliance confirmations
Review of Requirements for Products and Services (AS9100D 8.2.3 / ISO 9001 8.2.3)
What organizations must achieve
- Ensure all functions (sales, engineering, quality, production, supply chain) agree the requirements can be met.
- Identify gaps, conflicts, or risks before acceptance
Practical methods
- Cross‑functional review meetings for complex orders.
- Feasibility analysis for tolerances, materials, lead times, and capacity.
- Configuration review to ensure correct drawing revisions and specifications.
- ERP‑driven review gates that prevent job release until review is complete.
Required records which may be generated and/or maintained with QMSCAPA
- Signed contract review forms or electronic approvals.
- Feasibility assessments.
- Revision verification records.
- Capacity or scheduling confirmations.
- Notes from cross‑functional review meetings.
Coordinating the Review with Applicable Functions
What organizations must achieve
- Prevent “sales‑only” commitments that production or quality cannot meet.
Practical methods
- Electronic workflow requiring approvals from engineering, quality, and operations.
- Gate reviews (e.g., Gate 1: Sales; Gate 2: Engineering; Gate 3: Quality).
- Integrated ERP/PLM systems (QMSCAPA software) that enforce multi‑department review.
Required records
- RACI matrix or responsibility assignment documentation.
- Workflow approval logs.
- Gate review checklists.
- Evidence of cross‑functional communication (meeting notes, emails, ERP logs).
When Requirements Cannot Be Met (AS9100D 8.2.3.1 / ISO 9001 8.2.3.1)
What organizations must achieve
- Identify any requirement that is unclear, unrealistic, or impossible to meet.
- Negotiate a mutually acceptable alternative before accepting the order.
- Prevent unapproved deviations or assumptions.
Practical methods
- Technical clarification forms documenting questions and customer responses.
- Revised quote or contract amendment reflecting the negotiated change.
- Risk‑based decision making to determine whether to accept modified requirements.
- Customer approval of exceptions (email, signed form, or portal confirmation)
Required records which may be generated and/or maintained with QMSCAPA
- Revised quotes, purchase orders, or contracts.
- Clarification logs.
- Updated TDP or controlled documents.
- Risk assessments supporting the decision.