Including Customer Complaints
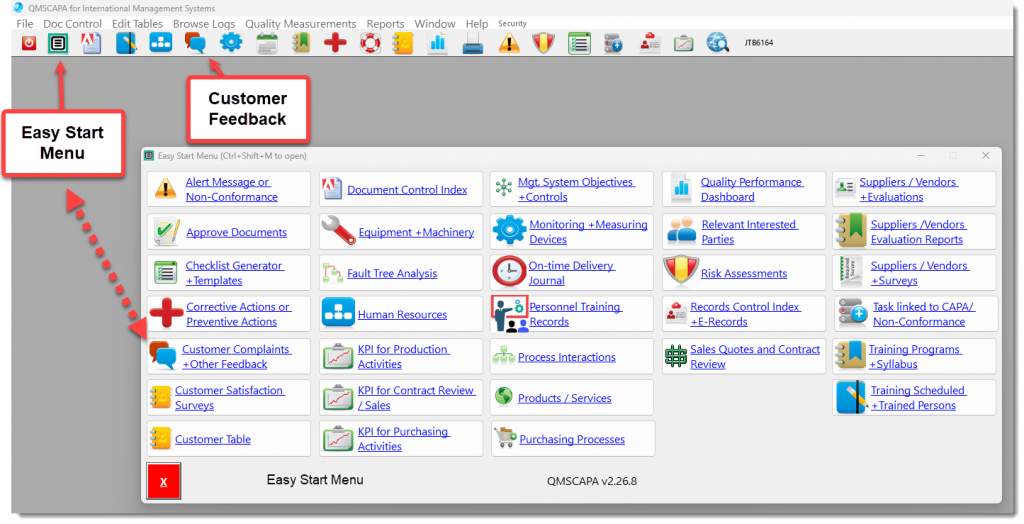

QMSCAPA software can be used for recording non-conformances. It includes a module specifically for logging non-conformances, allowing you to track and address quality issues within your organization.

Alert Incident Message
Non-Conformance Form
In AS9100D and ISO 9001:2015, the process approach plays a crucial role.
Let’s break it down:
Remember, the process approach involves risk-based thinking and follows the PDCA cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act) for continual improvement.

The QMSCAPA software module for Nonconformance and Corrective Action provides direct links to the following Quality Management Systems methods and processes:


These tools include direct links to the AIM Nonconformance Log.

QMSCAPA provides a robust module, method and process for meeting the requirements of ISO 9001 and AS9100, among others, which focuses on Clause 8 Operations:

Sales Contracts, Proposals, and Quotes are directly linked to the Customer module.

Use the Contract Review module for creating and maintaining documented information




We have completed many improvements for QMSCAPA to provide better performance when running inside a Windows Server with TSPLUS.
TSPLUS provides Remote Desktop Services through a secure connection with many modern browsers, including Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Mozilla Firefox.
In addition to supporting multiple-concurrent users and multiple tenants in a Microsoft Remote Desktop Server, QMSCAPA may be deployed using a Microsoft Server (2016R and higher) configured with TSPLUS.
This configuration provides a very high performance and stable working environment through the HTML5 architecture that works in all modern browsers.
The QMSCAPA application has been designed to run in Microsoft Windows, whether in a local Windows PC, Cloud PC, or Server, Virtual Machine or a Windows Server with Remote Desktop Services.
Also, these Microsoft Windows applications allow users to connect with devices using Apple and, or Android operating systems.

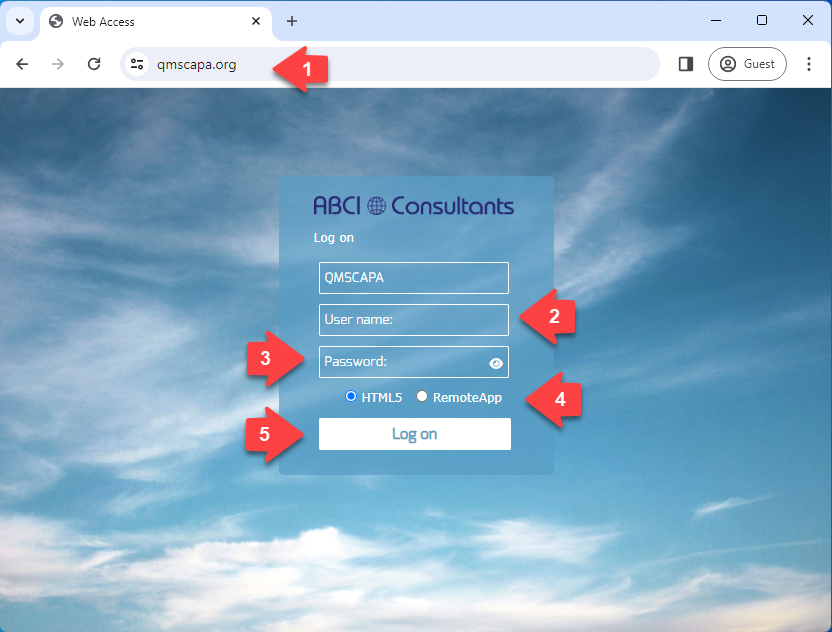
Using your favorite web browser:
Once you have successfully completed the login the Server Applications panel page will be displayed.
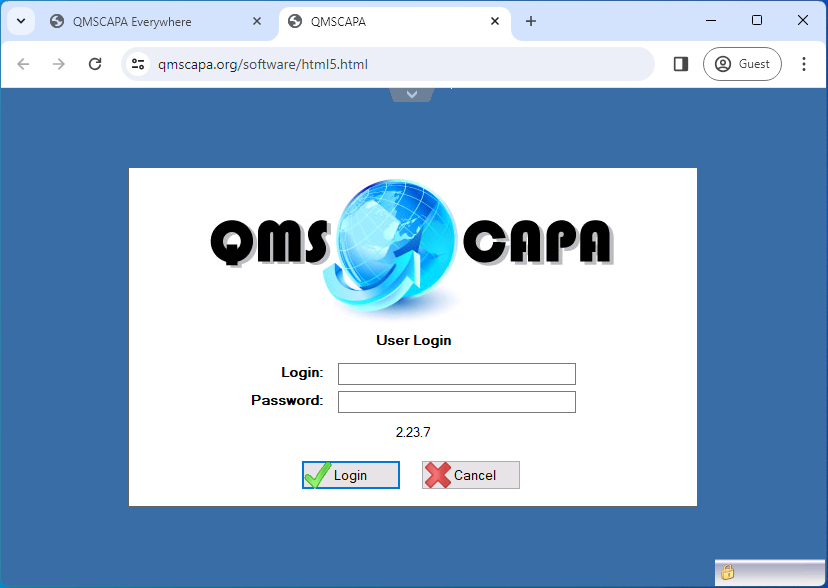
Enter your Login and Password assigned by your Domain Administrator. The QMSCAPA login and passwords are not case sensitive.
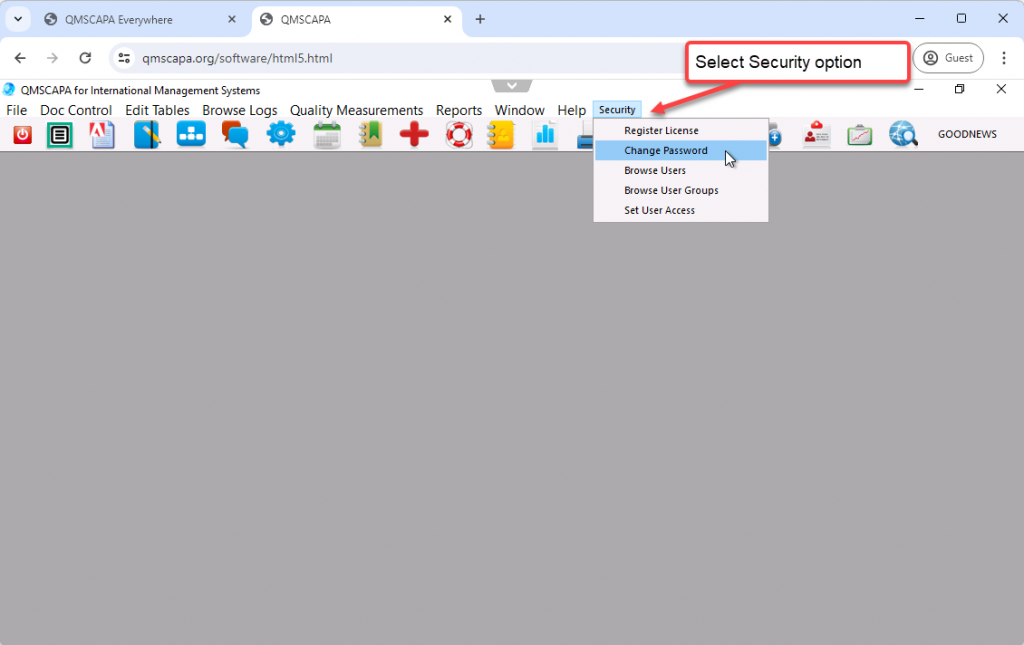
To change your password select the Security menu option and the Change Password option.
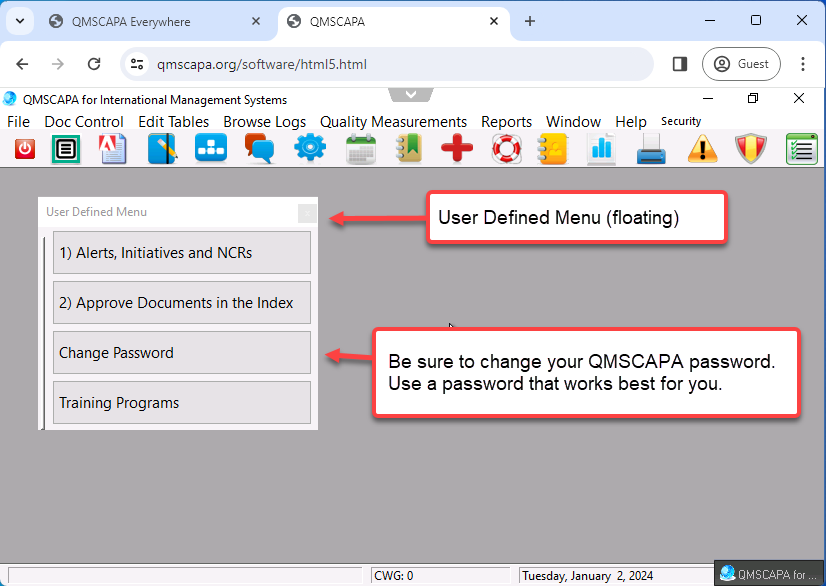
QMSCAPA has four application navigational methods, which are:
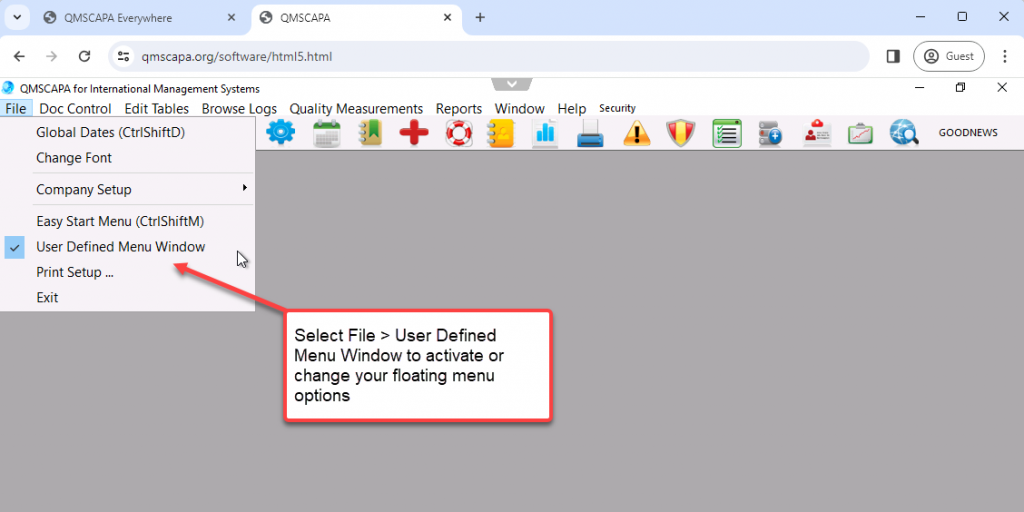

Your Domain Administrator may add one or more applications to the QMSCAPA host application panel.

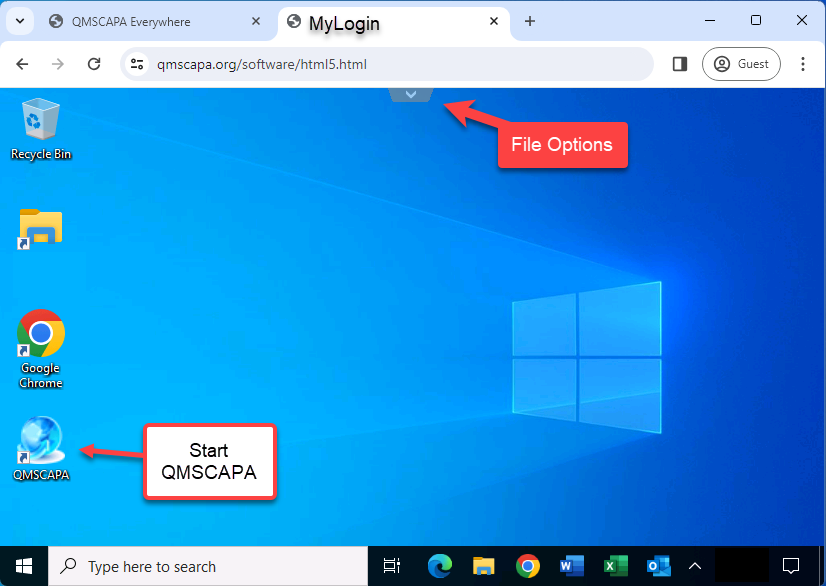
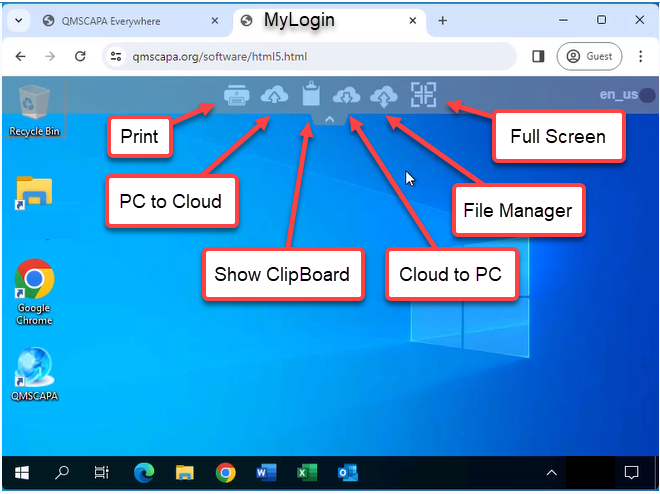
Click on the “v” or “^” at the top of the browser window to drop down File Management and Full Screen options.
Important enhancements and fixes have been made in a new release of QMSCAPA™ (version 2.22.1) and is available for download from QMSCAPA.app.
All of the Quality Monitoring and Measurements modules, browse tables and forms have been overhauled to simplify and streamline the entry and maintenance processes.
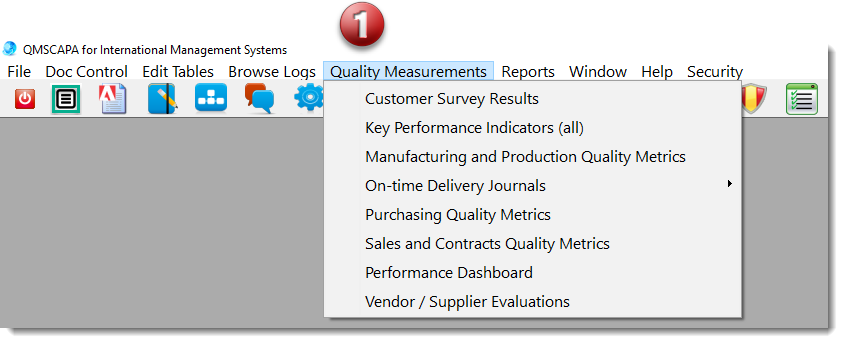
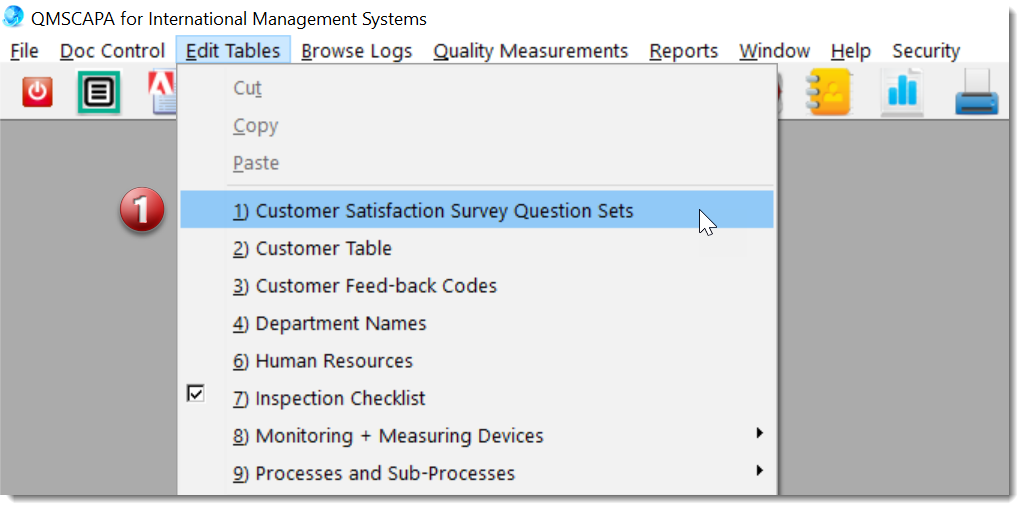
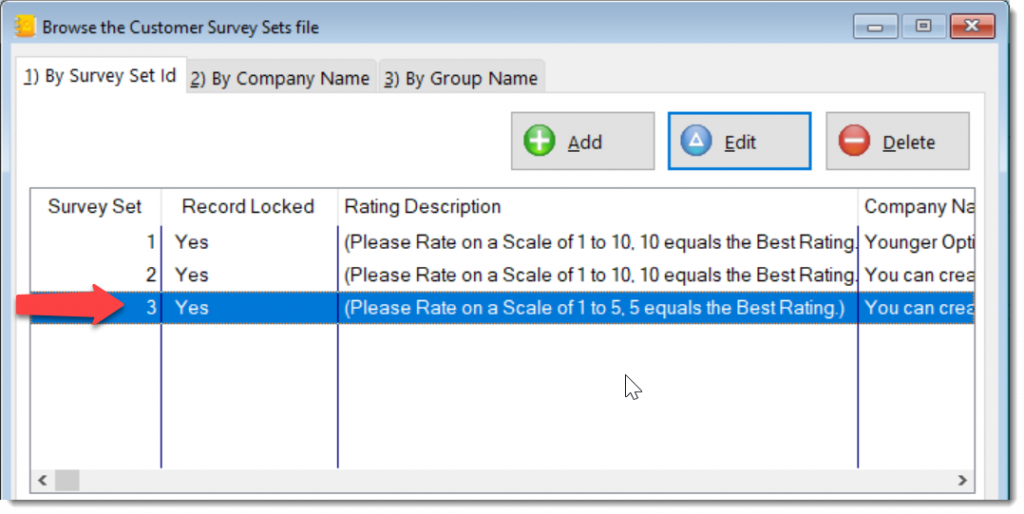
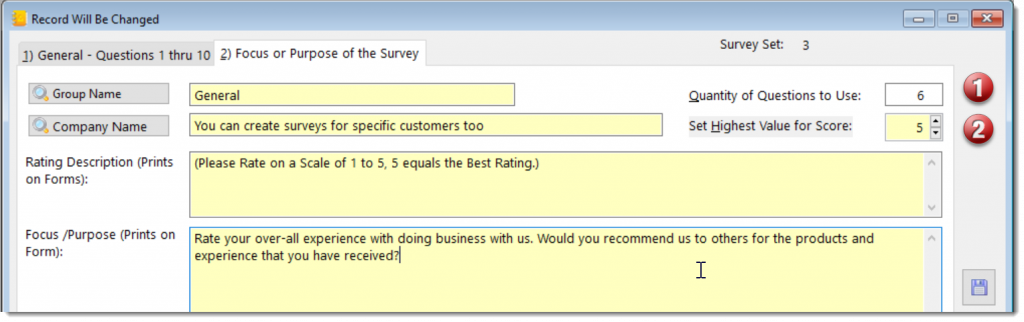
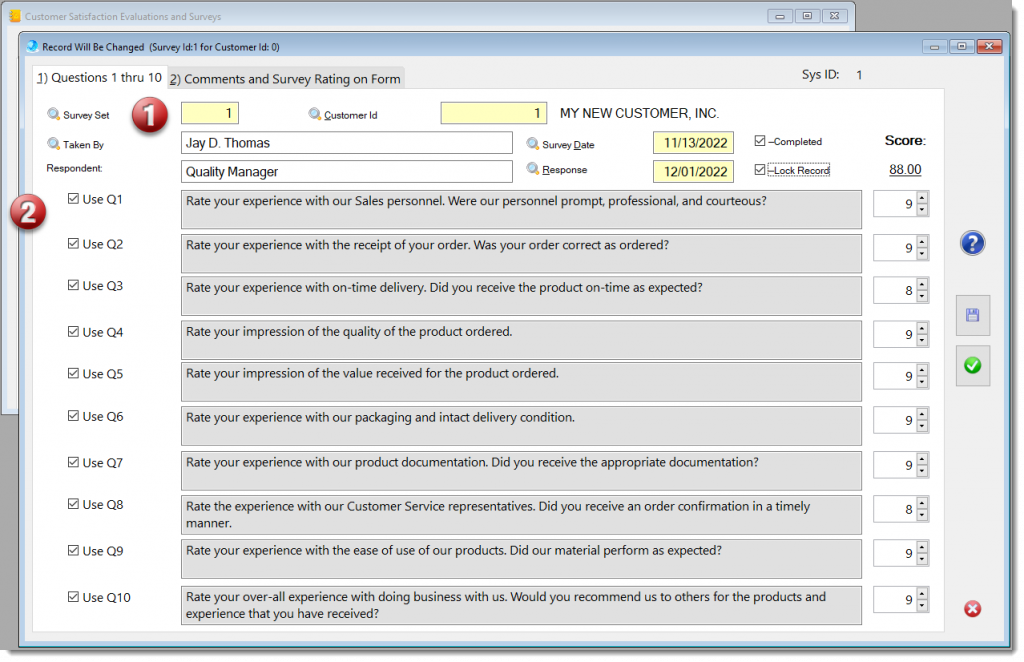
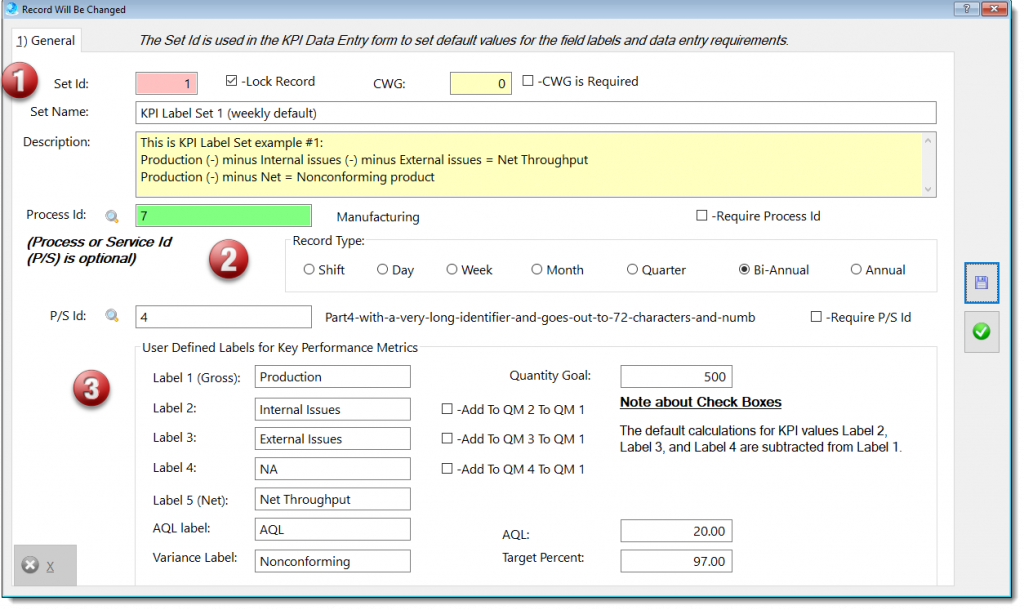
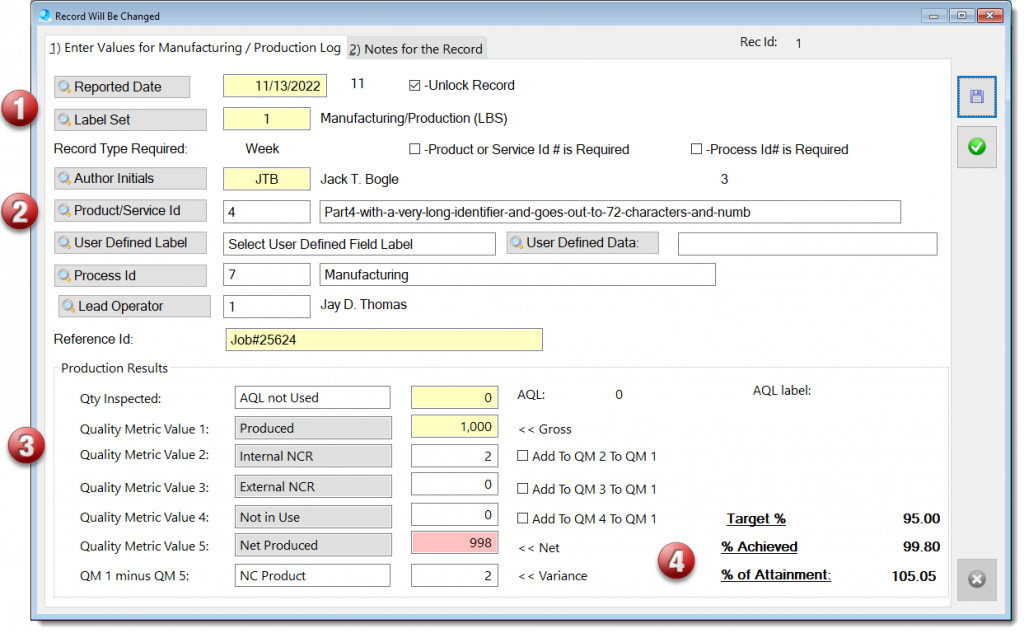
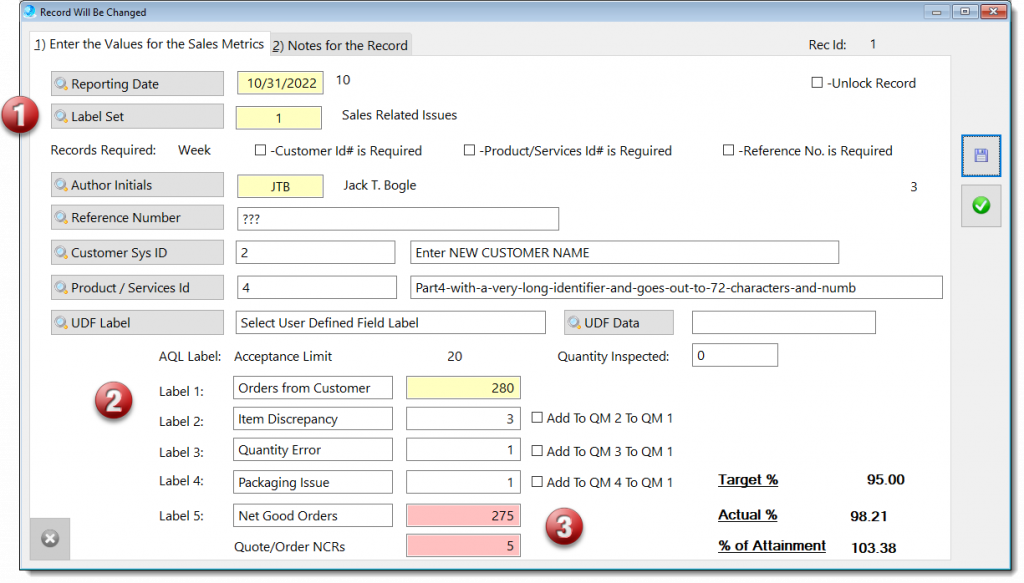
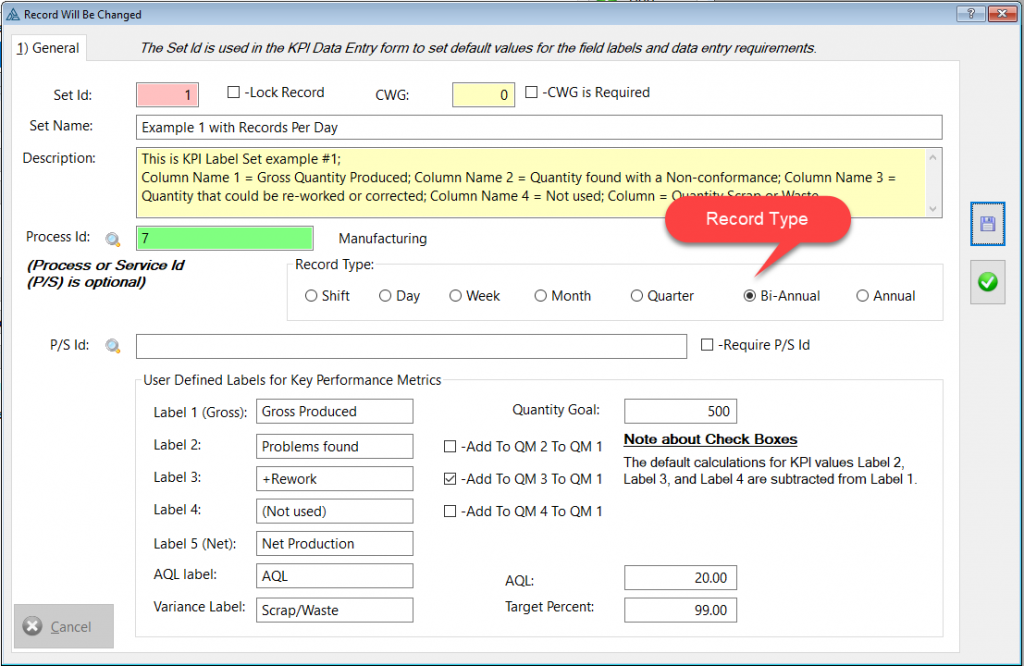
This generic measuring module may be applied to any process that should be monitor by key performance indicators (KPI).
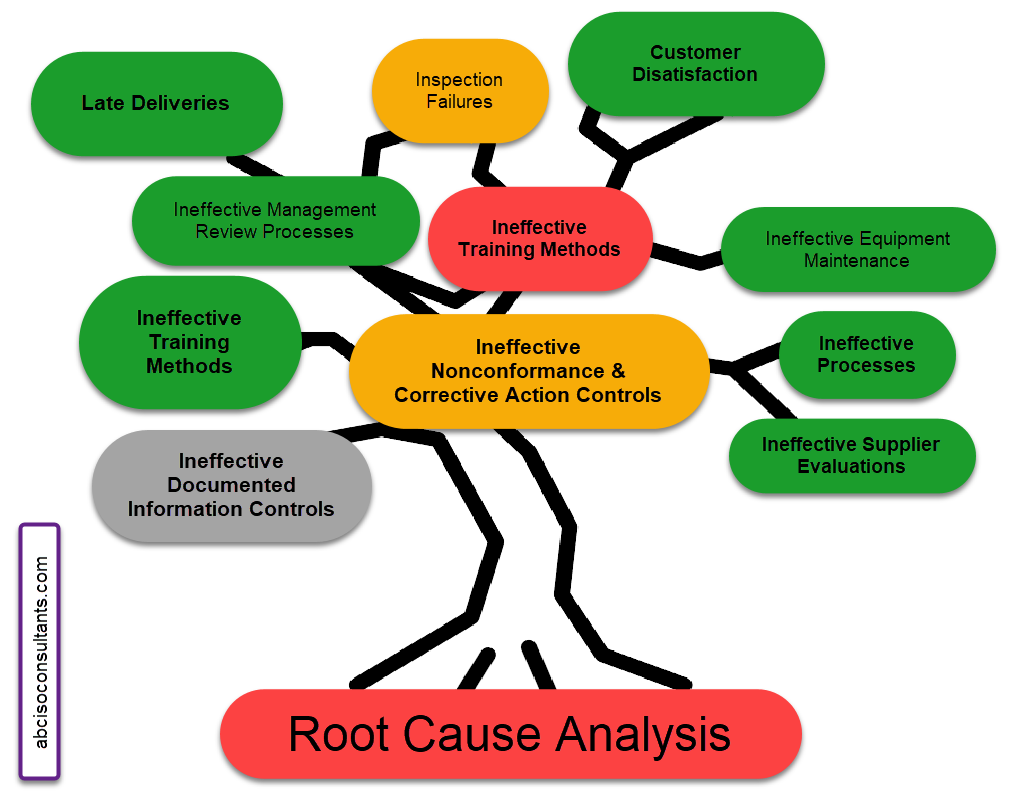
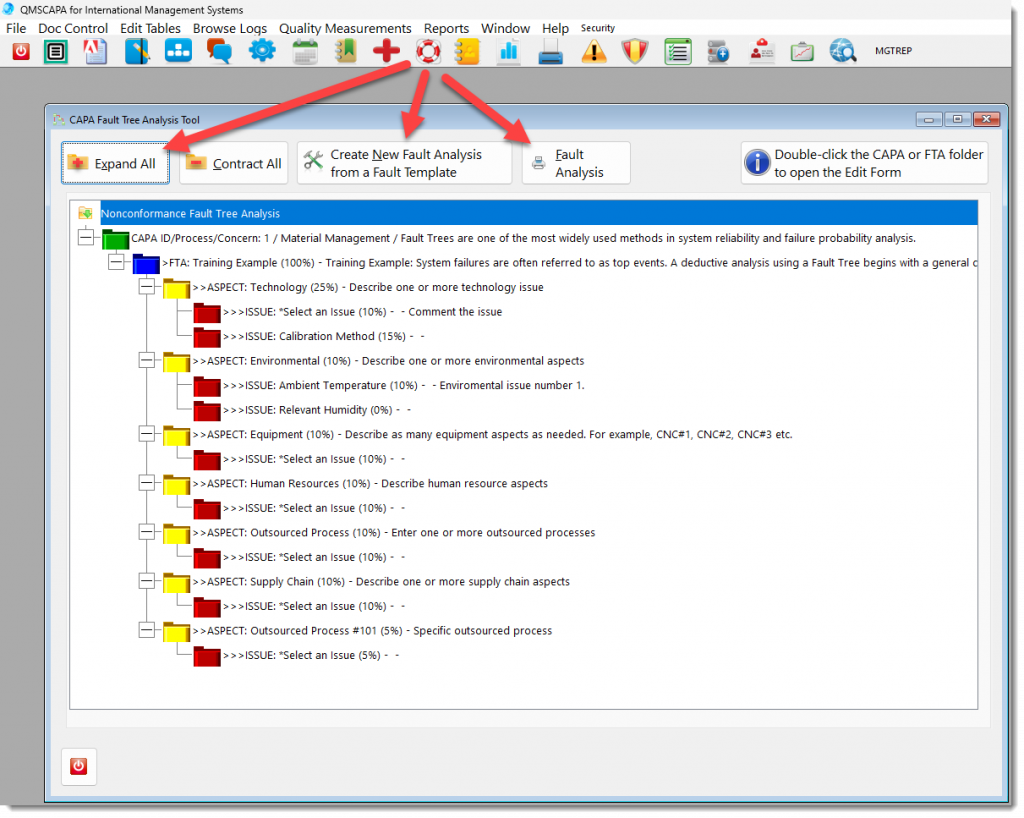
The QMSCAPA “Fault Tree Analysis” tool is built right inside the QMSCAPA software module for Corrective Actions.
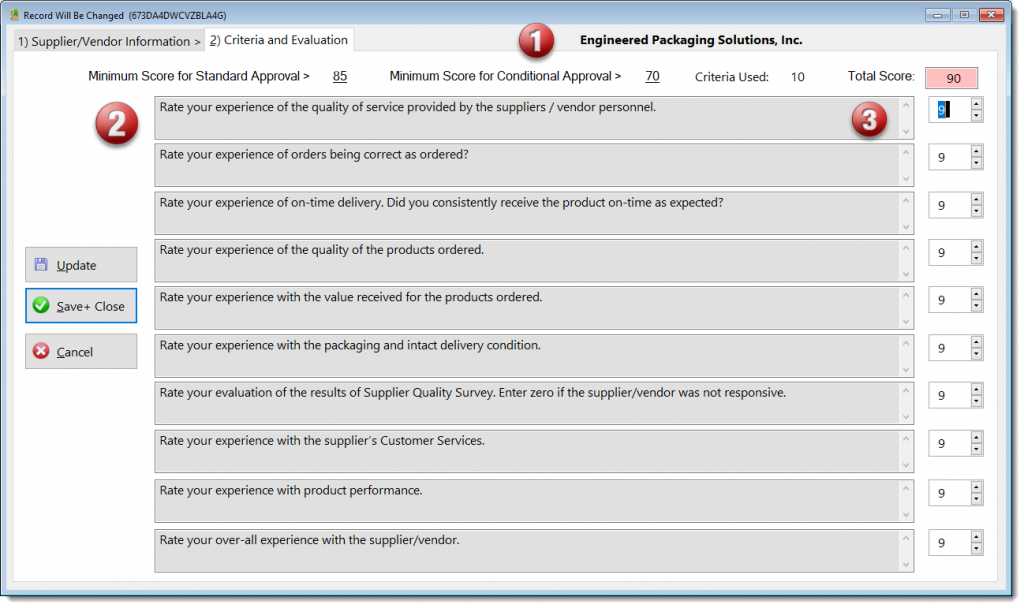
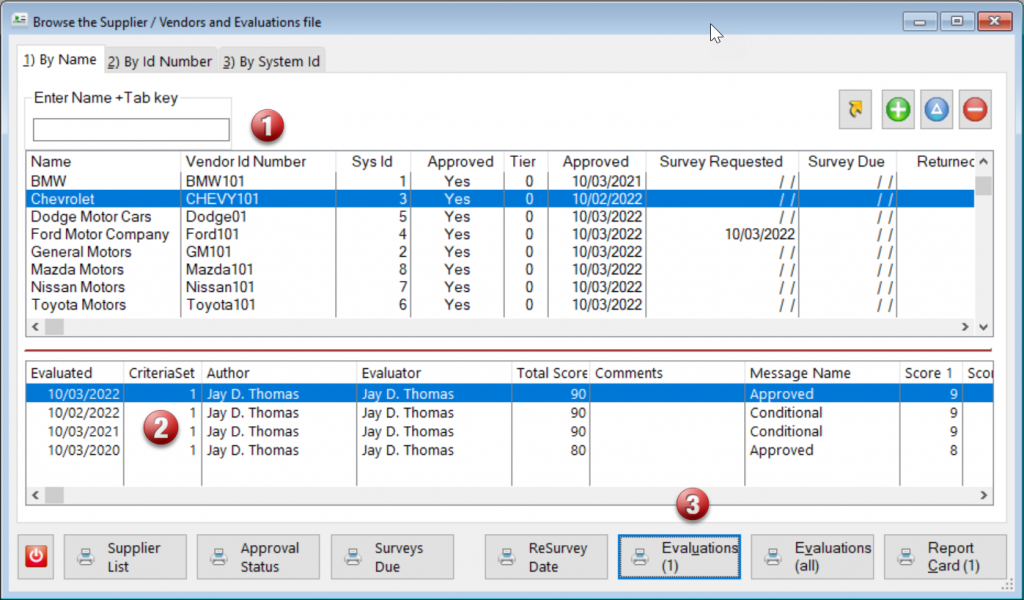
Supplier or Vendor Evaluations, based upon the “Ten Squared” method, which includes a criteria of 10 evaluated on a scale of 1 to 10.
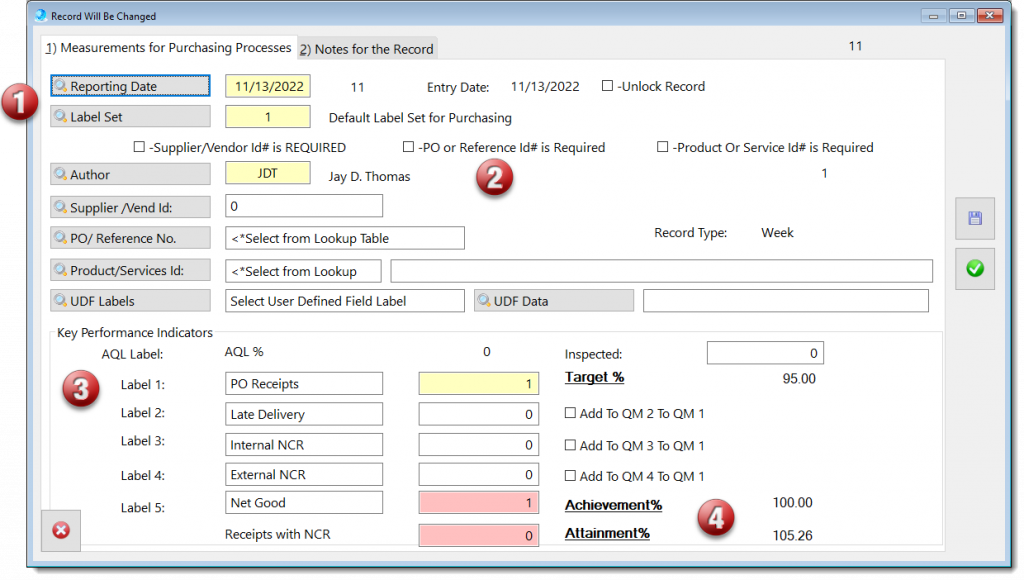
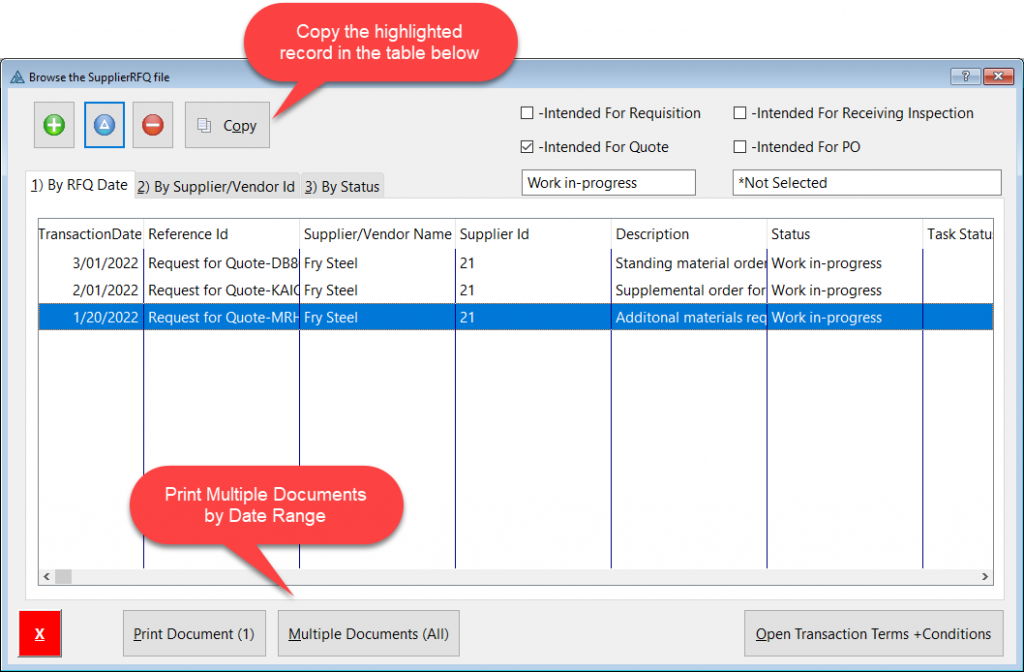
The Purchasing Processes module provides a method for managing purchasing transactions, which incudes:
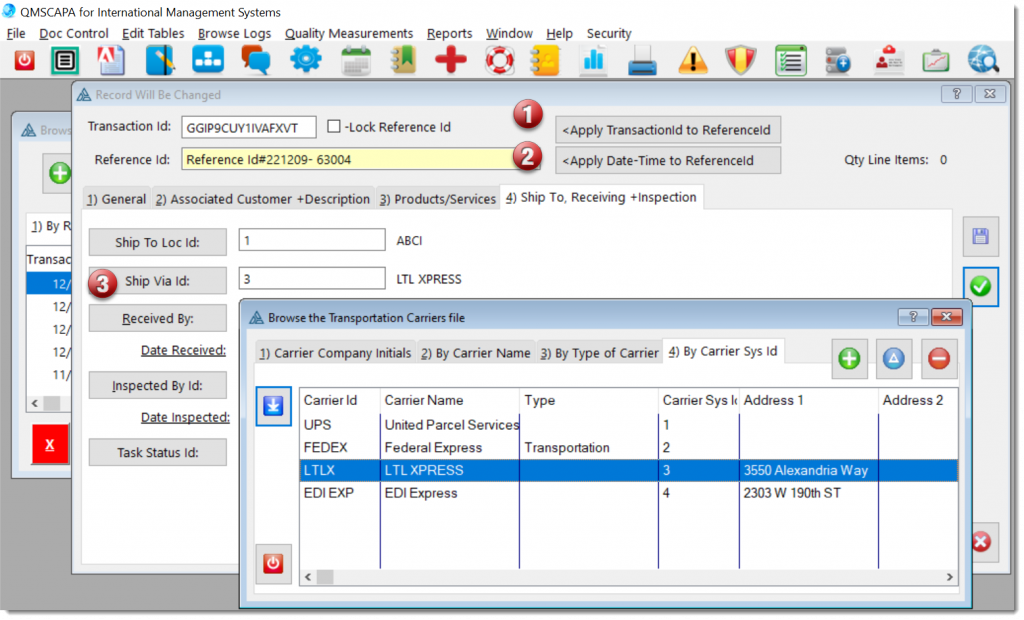
In the imagine above:
Important additions, enhancements and fixes have been made in a new release of QMSCAPA™ (version 2.18.10) and is available for download from QMSCAPA.app.

Important additions, enhancements and fixes have been made in a new release of QMSCAPA™ (version 2.17) and is available for download from QMSCAPA.app.
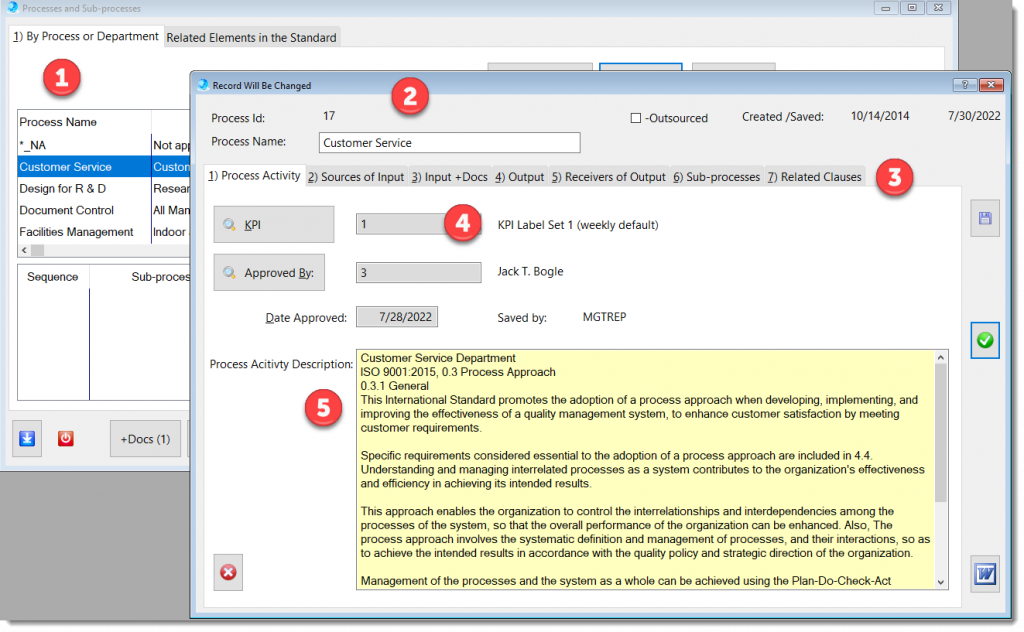
In the ISO 9001:2015 International Standard, among other (Aerospace, Automotive, and ISO) Standards, promotes the adoption of a process approach when developing, implementing, and improving the effectiveness of a quality management system, to enhance customer satisfaction by meeting customer requirements.
Specific requirements considered essential to the adoption of a process approach are included in ISO 9001:2015, section 4.4. Understanding and managing interrelated processes as a system contributes to the organization’s effectiveness and efficiency in achieving its intended results.
This approach enables the organization to control the interrelationships and interdependencies among the processes of the system, so that the overall performance of the organization can be enhanced.
Also, the process approach involves the systematic definition and management of processes, and their interactions, so as to achieve the intended results in accordance with the quality policy and strategic direction of the organization.
The application of the process approach in a quality management system enables:
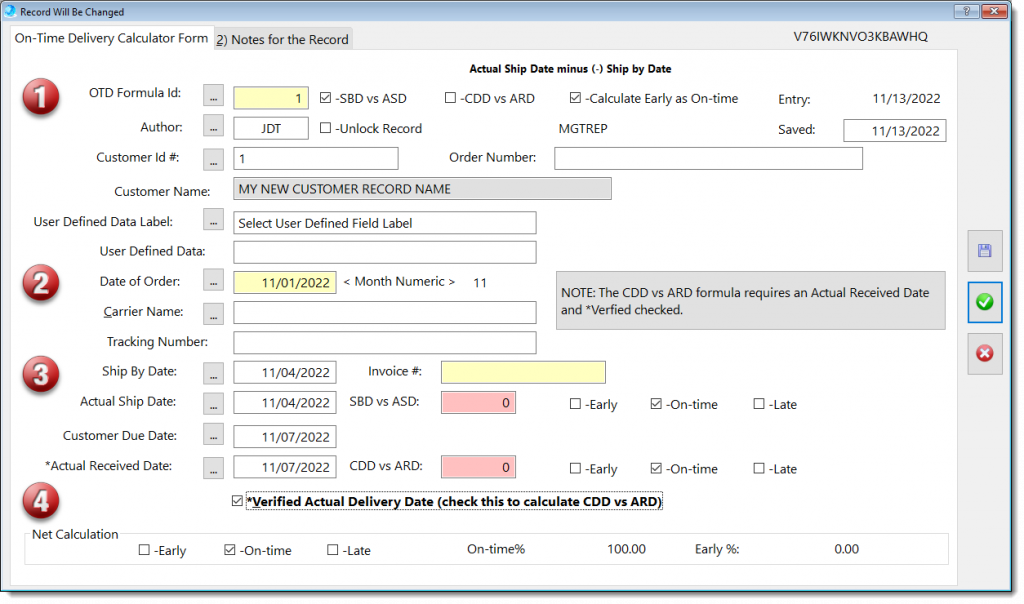
In the image above:

#End-of-post
Important additions, enhancements and fixes have been made in a new release of QMSCAPA™ (version 2.16.12) and is available for download from QMSCAPA.app.
AnyText allows a user to change the text in a QMSCAPA Window at runtime. Most of the visible text, including Window Captions, Prompts, Buttons and so on can be translated.
This allows a Supervisor User to create multi-language or special vernacular versions of QMSCAPA application.
It also allows users to change terminology inside a program, even if they are using the same language. This helps to make the program more familiar to users. For example in some countries you would use a ZIP CODE in an address, whereas in others this is known as a POSTAL CODE.
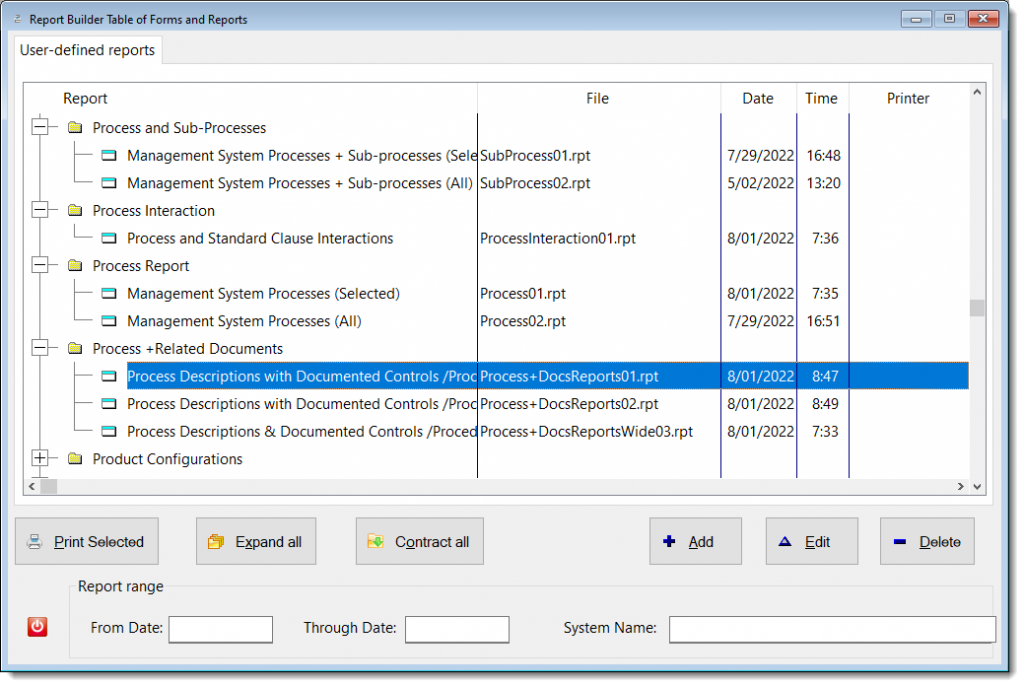
The Default Document/Manual report template was updated to include more “user-defined” information, which may appear inside the DCI and any document grouped defined by a user, such as by category, type, and standard.
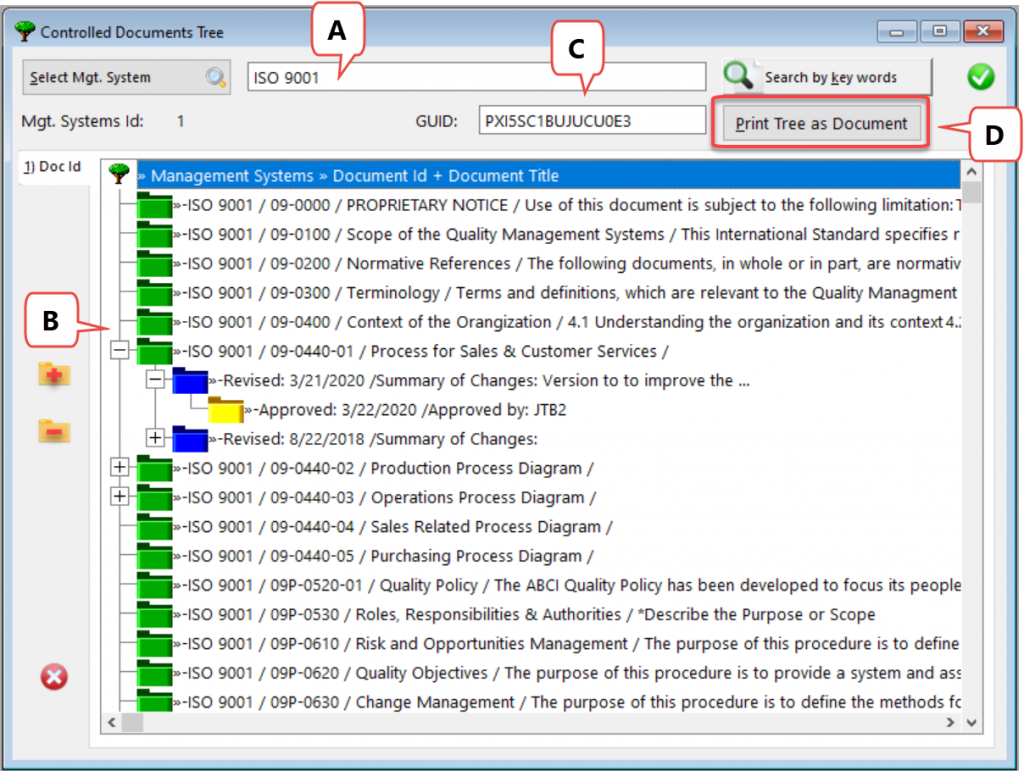

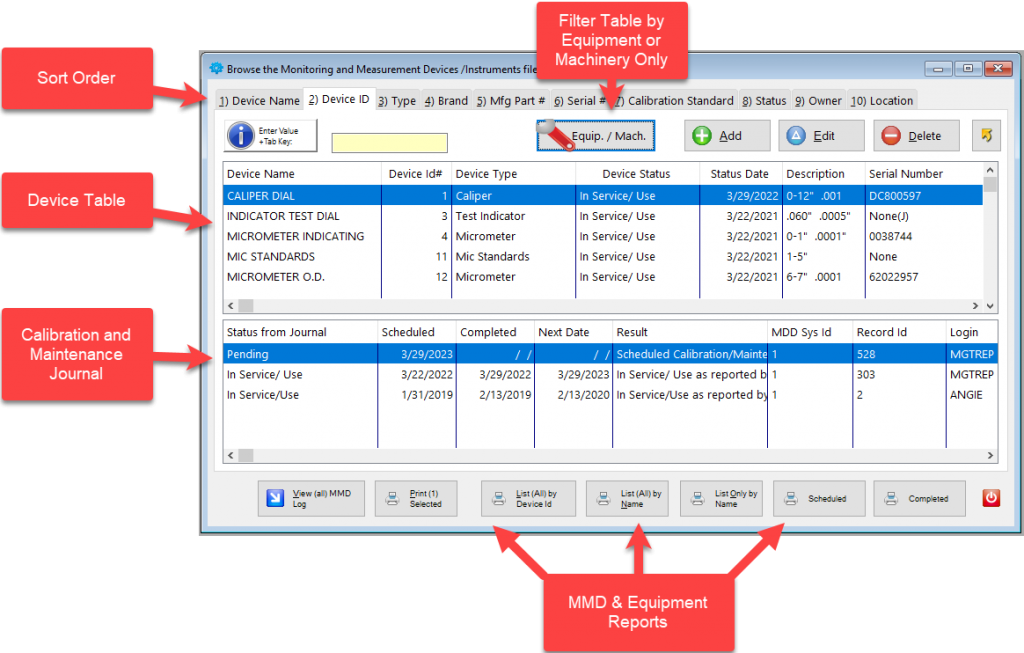
Important enhancements and fixes have been made in a new release of QMSCAPA™ (version 2.15.1) and is available for download from QMSCAPA.app.

The Internal Audit module is designed to asist with the planning and record keeping to provide information on whether the management system a) conforms to:
b) is effectively implemented and maintained.
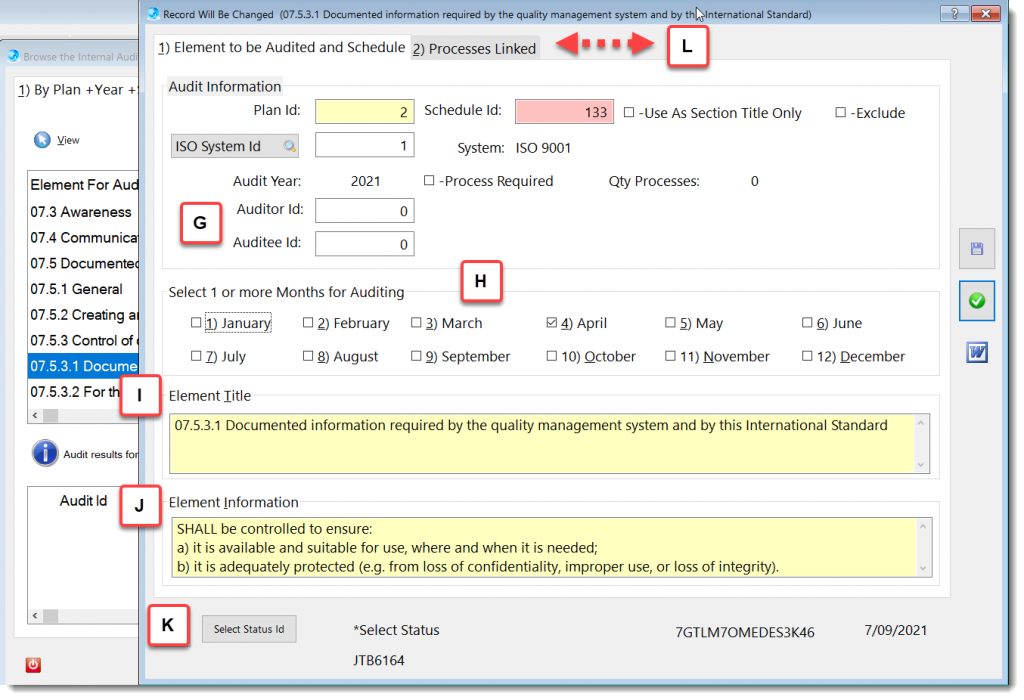
More about QMSCAPA Internal Audit Planning module …

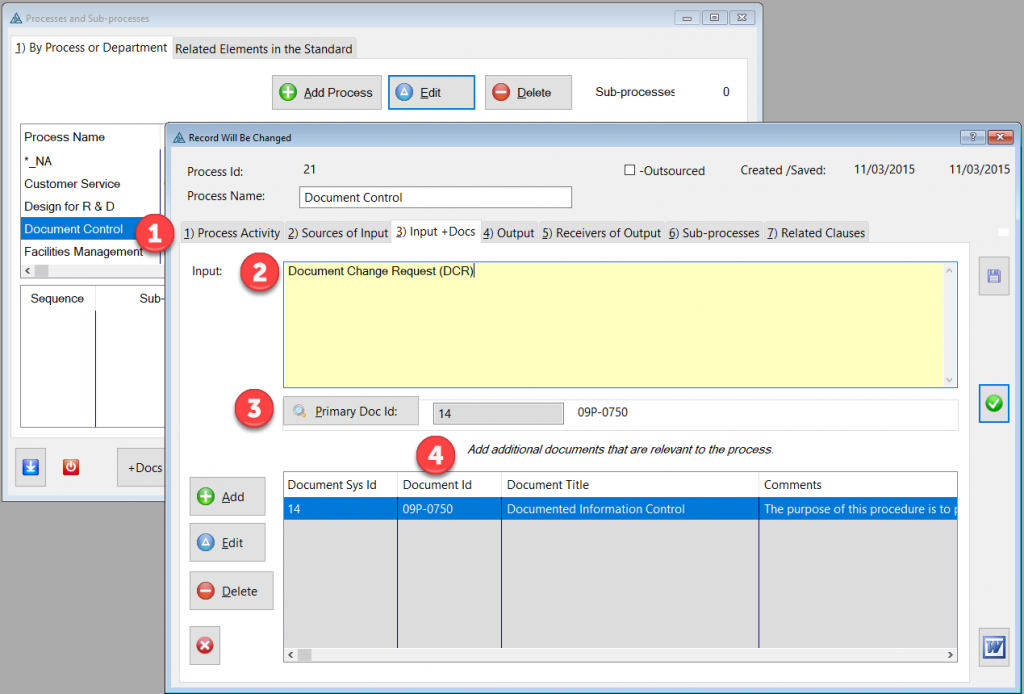
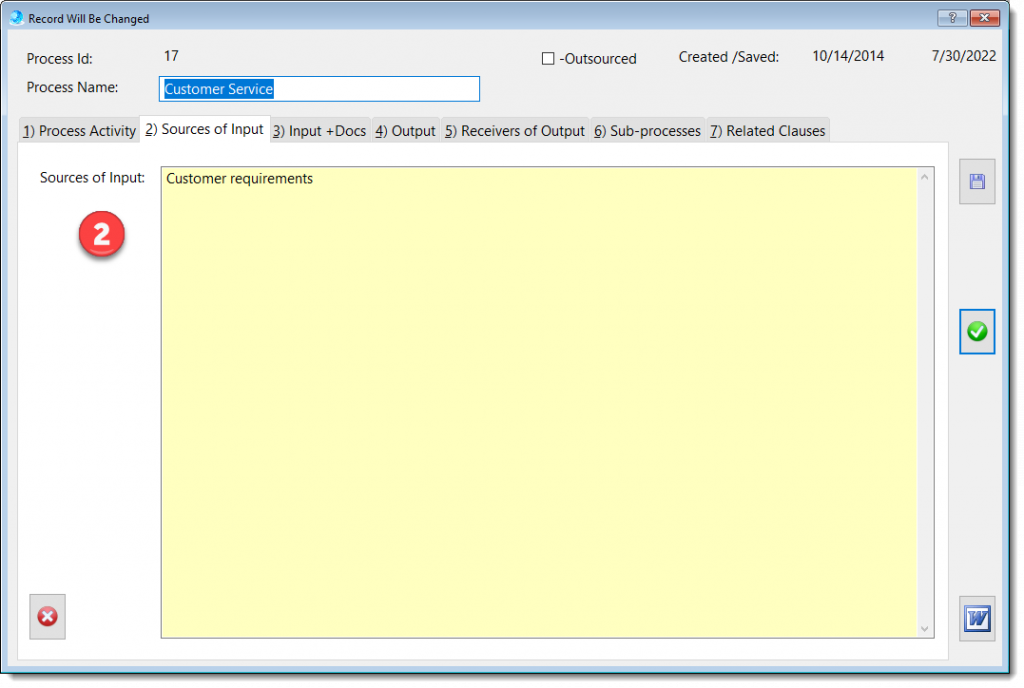
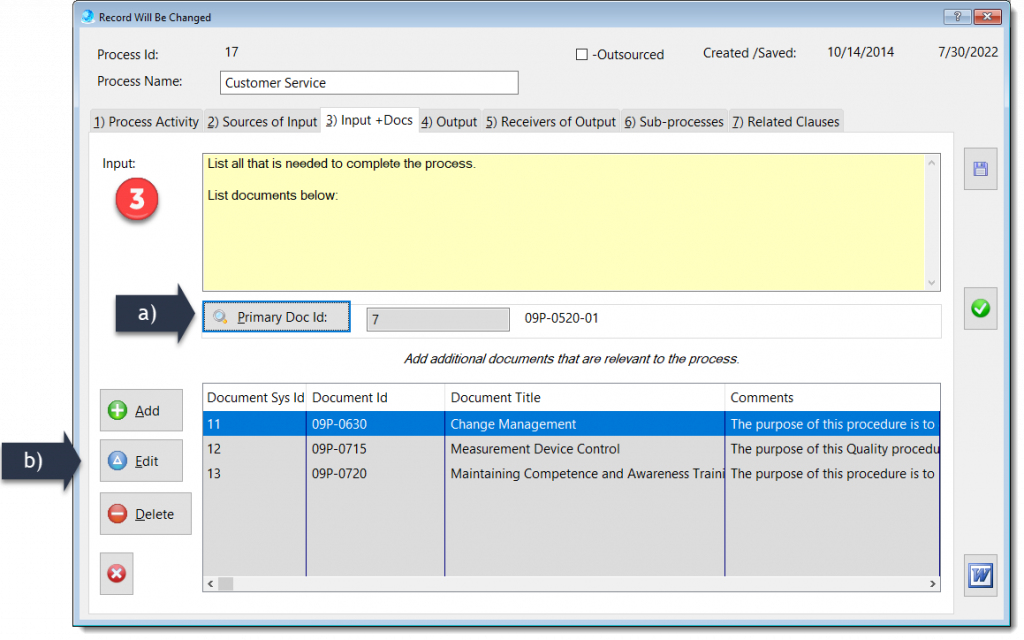
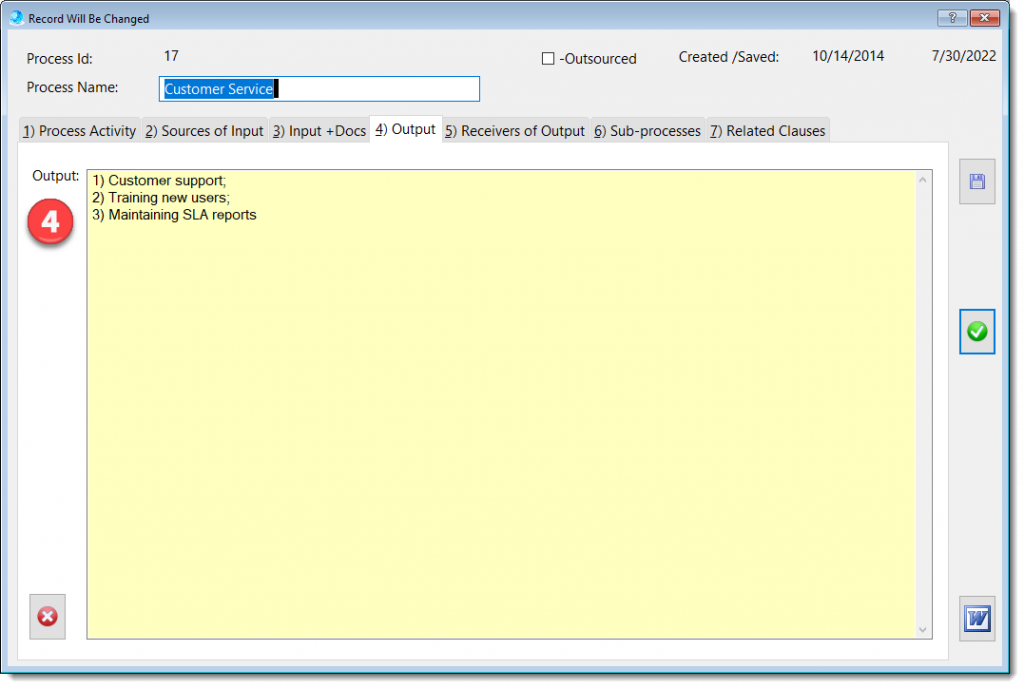
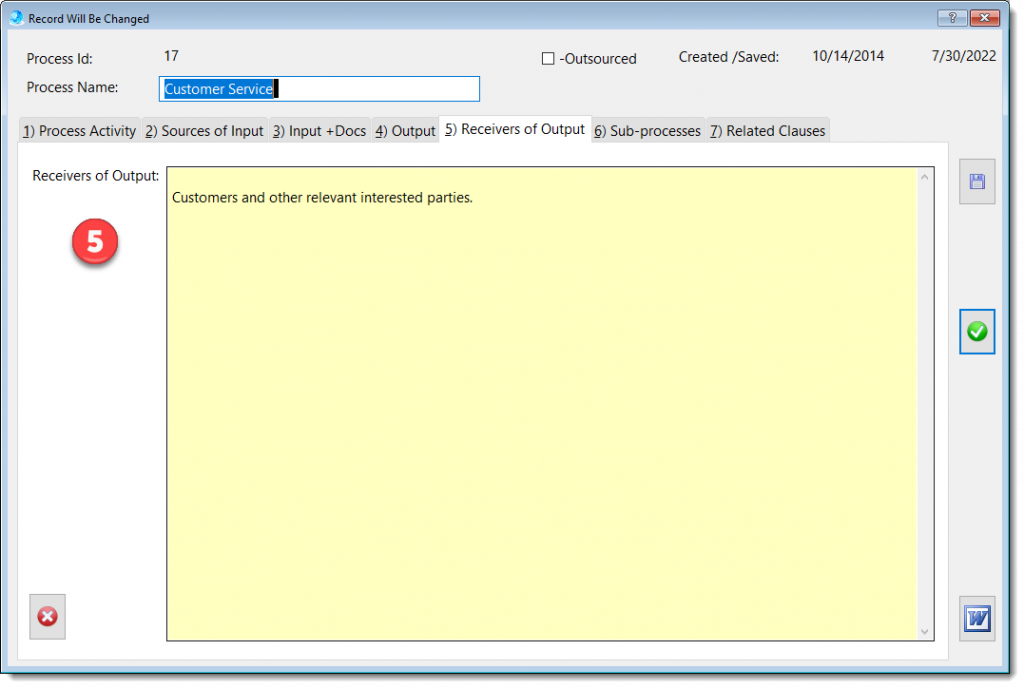
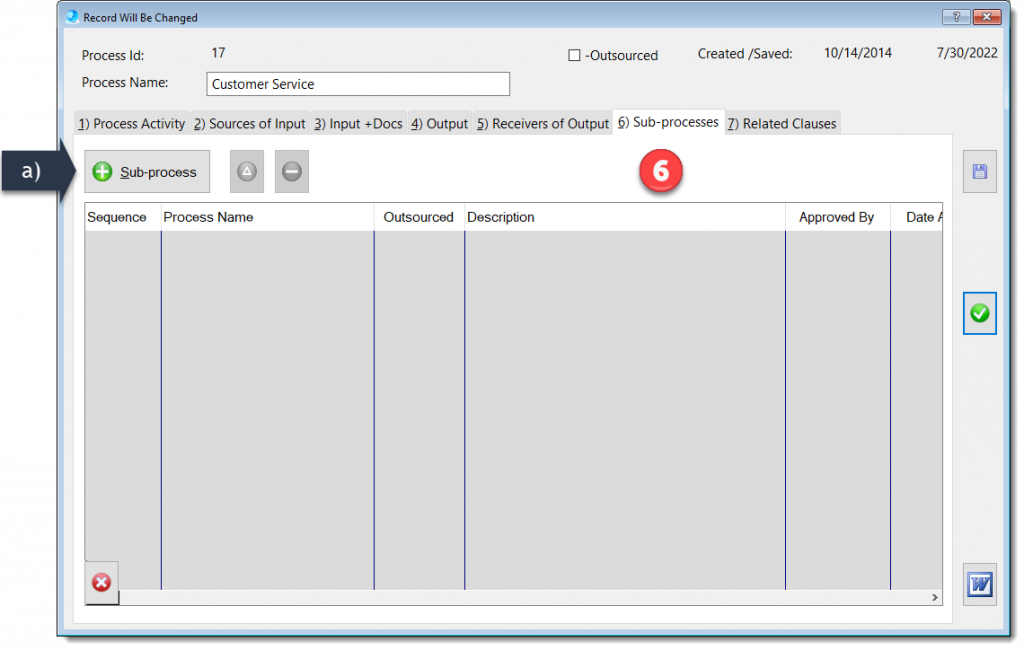
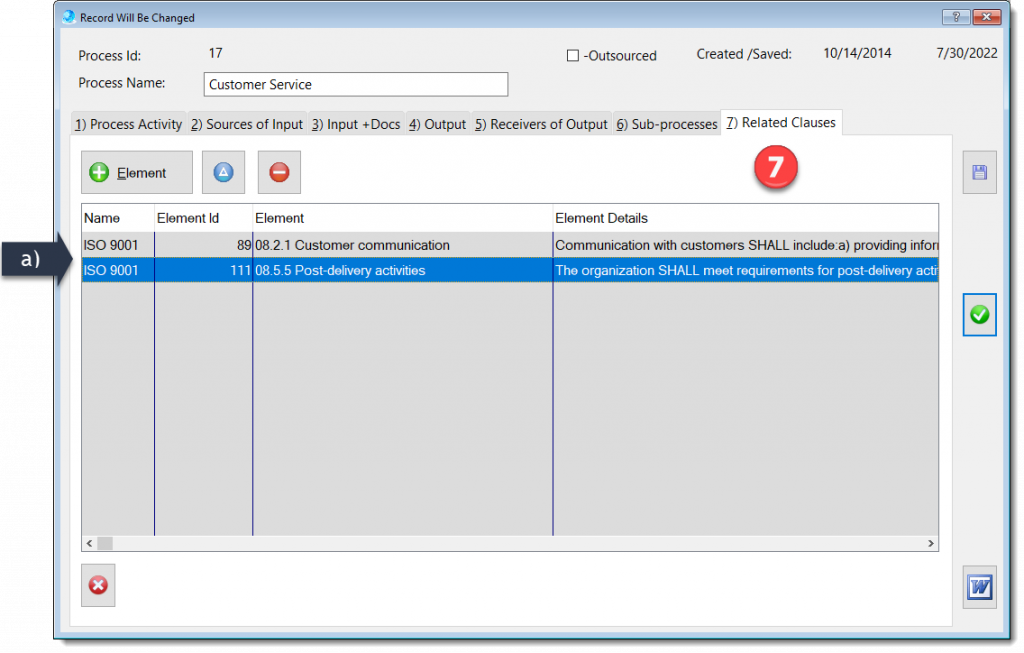
The Process Description and Mapping module is designed to assist with establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improve a management system, including the processes needed and their interactions, in accordance with the requirements of this International Standard.
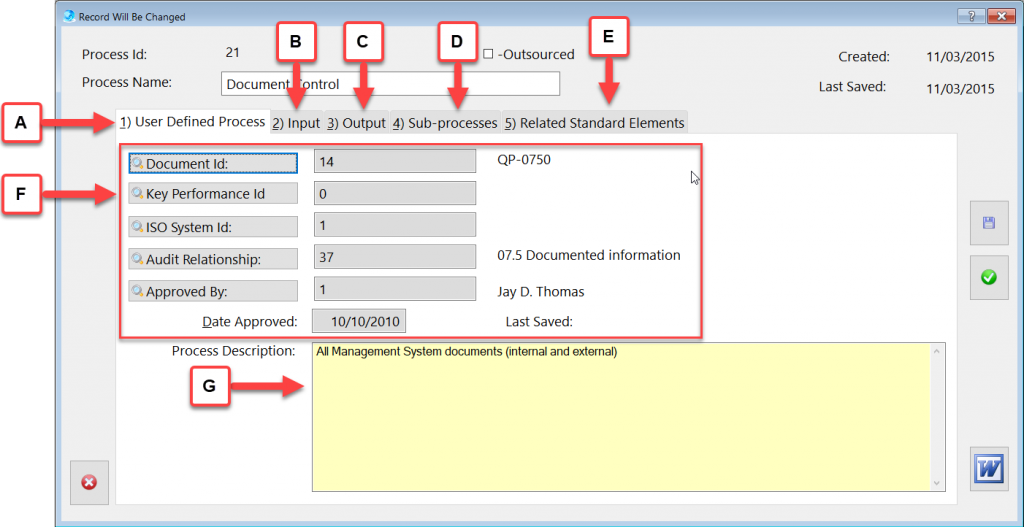
More about QMSCAPA Process Description and Mapping module …