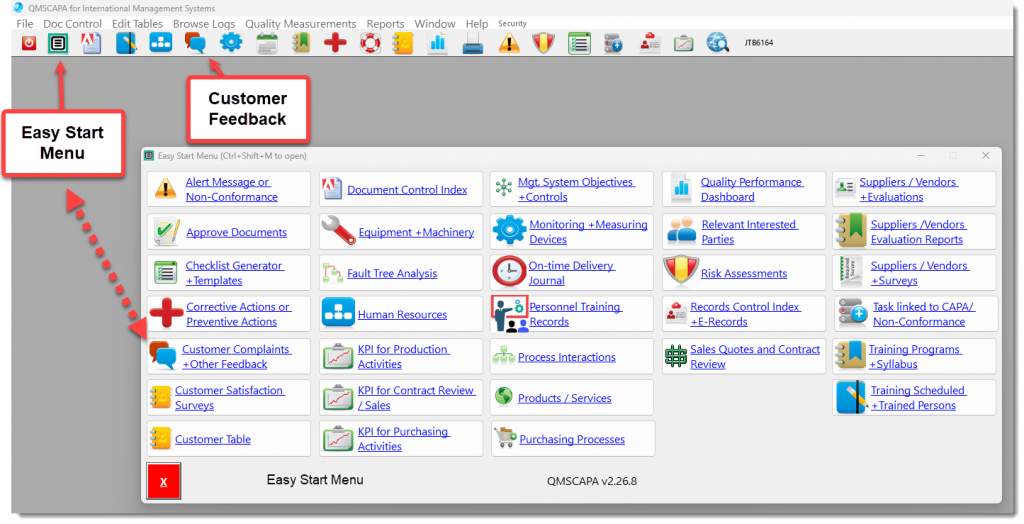
Windows Remote Desktop Services (RDS)
Platform: Primarily Windows-based, with support for Mac and Linux via third-party solutions.
Deployment: On-premises or cloud-based via Azure.
Security: Advanced security features including SSL encryption, Network Level Authentication (NLA), and continuous access evaluation policies.
Performance: Optimized for hosting applications and desktops with RD Session Host Configuration.
Management: Integrated with Active Directory for user and group management, and enhanced RD Licensing Management.
Pricing: Typically part of a Windows Server license, with additional CALs required.
TSPLUS®
Platform: Supports Windows 10, 11, Windows Server, Mac, Linux, SaaS, and Web-based solutions.
Deployment: On-premises or cloud-based, with a focus on ease of deployment.
Security: Offers SSL encryption and smart card authentication for secure remote access.
Performance: Known for its ease of use and quick setup, making it suitable for small to medium-sized businesses.
Management: Provides centralized management for remote access, application delivery, and remote printing.
Key Differences
Platform Support: TSPLUS offers broader platform support compared to RDS.
Deployment Flexibility: TSPLUS is often praised for its ease of deployment and setup.
Security Features: Both offer robust security features, but RDS has more advanced options integrated with Windows Server.
Management Tools: RDS is deeply integrated with Windows Server management tools, while TSPLUS offers a more streamlined approach.
Ultimately, the choice between RDS and TSPLUS depends on your specific needs, such as platform requirements, deployment preferences, and budget.